Besides a variety of efficient renewable energy such as hydroelectricity, geothermal power or biomass, solar power has currently been widely used in both industrial infrastructure as well as home electrical system. After various developments since solar power was invented in the 1860s, because of the increase in solar and battery storage system, the idea of trading the excess of electricity generated from solar power between households was raised, which eventually formed an energy trading system called Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Energy Trading. Nowadays, this concept is becoming more and more popular due to the efficiency and the profit it brings to prosumers.

I. Understanding Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading
1. What is Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading?

Infinite Energy (2019) defined the term “Peer-to-Peer (P2P) energy trading” as an exchange of excess energy, which is often in the form of solar energy, between grid-connected parties. Basically, according to Barbara Albert (2018), P2P energy trading is similar to the data sharing programs on the Internet or various shopping platform such as Amazon, eBay, etc. With this new concept of trading energy, energy or more specific, electricity has become a commodity. Therefore, consumers are allowed to make the decision to choose either whom they want to purchase the energy from or who they want to sell it to. Mandela (n.d) indicated that thanks to the P2P energy trading concept, the electricity prices in the energy market can be effeciently maintained competitive.
2. Historical background
According to Infinite Energy (2019), the first trade relating to energy between local residents was conducted by a household with solar power system in New York in 2016 via the Etherum blockchain.
After that event, the idea of making profit from selling energy, espcially electricity, has circulated all over the world. Currently, there is lots of diffent start-ups or companies which are participating in this potential field.
LO3 Energy, Inc
LO3 Energy, Inc is a technology company, which specialize in distributed energy, with its headquarter placed in Brooklyn, New York. By creating and operating a platform called Exergy, LO3 aims to develop the localized marketplaces for trade in excess energy across existing grid. In addition, this company is building a blockchain-based platform to carry out decentralized business models and innovative technologies involving in energy system and utility systems.

Greensync with the deX project
Greensync is a global energy-tech company establishing connections of energy resources to make existing grids more dynamic. In December 2017, ‘Decentralised Energy Exchange’ or deX, a digital platform which exactly indicates the availability of different distributed energy at anytime on customers’ premises, was launched. In particular, deX create an open marketplaces for distributed energy services to be generated, controlled or stored, and then traded between households, businesses, utilities and the larger market operators.

3. How does P2P energy trading work?
Let’s take the SunContract platform as a clear example of the way P2P energy trading works.
SunContract Energy Trading System
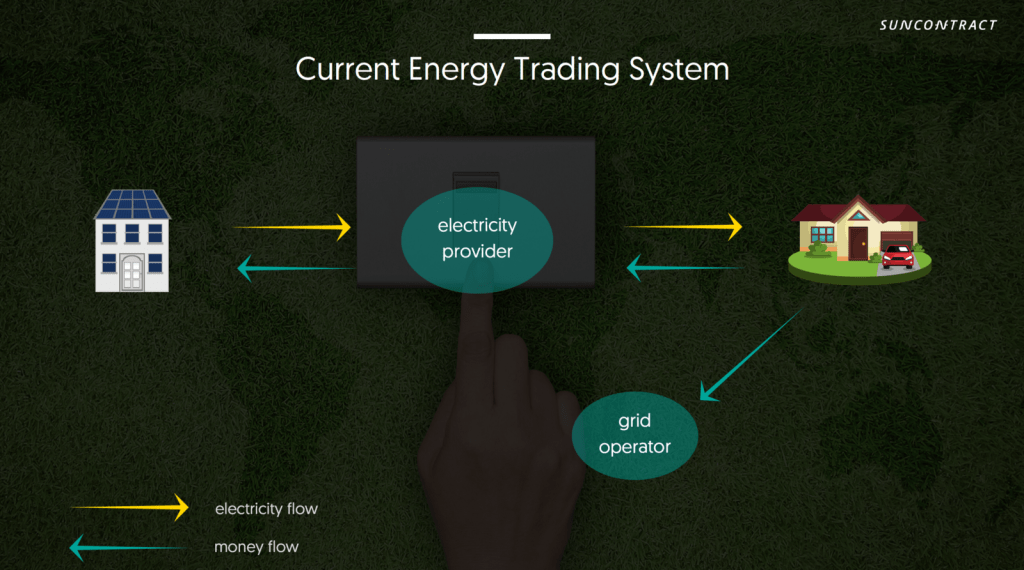
The image above simply illustrates the overview of how an energy trading system operates based on SunContract trading platform. Normally, a middleman company would purchase electricity from a producer at a less than optimal price, then sell it to consumers with higher prices to turn a profit. However, with SunContract transaction system, the producer and consumer are directly connected to conduct the trade via an agreement. As a result, the consumer can purchase electricity at a more reasonable price with the same quality and the producer can earn more money when directly selling the generated electricity to consumers rather than a middleman company. By this method, consumers are able to effectively control their electricity cost savings while the business of producers become more profitable.
But what types of necessary hardware as well as software components we need to establish a P2P energy trading system? And how blockchain relates to P2P energy trading? Let’s figure them out.
Hardware
Because most of excess electricity now are generated by using solar power, we need suitable technologies and devices to produce that type of energy.
Solar panels (Solar batteries)
Solar panels function as devices which are capable of capturing the sun energy and converting it into DC electric current. A solar panel is a combinatione of a lot of solar cells, which are usually made of silicon. A solar array is formed when a number of solar panels are wired together. Working as a battery, solar panels can not only generate DC electricity but also store it.

Solar Inverter
After taking DC electricity from solar array, solar inverter will turn it into AC electricity. In addition, an inverter also provides producer with system stats including voltage on DC and AC circuits and the amount of generated energy. Nowadays, micro-inverters are becoming more and more popular thanks to their ability to effectively maintain the operation of a solar system array even when a solar panel is broken.

Software
As the report mentioned above, the first electricity transaction was conducted using the Etherium blockchain. So, what is blockchain and how does blockchain affect P2P energy trading?
Blockchain and Smart contract

Have you ever heard about cryptocurrency such as Bitcoin? Blockchain is the record-keeping technology or in particular, a secure database behind those cryptocurrency. Because of being a secure database, blockchain are widely used in different field such as real estate, banking, cryptocurrency and even P2P energy trading.
Traditionally, traders need to draft contracts and communicate with their customers directly whenever trading energy. Many contracts can become complicated because traders have to contact each other via email or phone. Therefore, this is a time-consuming, inefficient and expensive process.
However, with the new blockchain technology, traders can sell or buy energy without performing those several steps of communication with another trader by using the implementation of smart contract.
According to Investopedia (2019), a Smart contract is a computer code which are built into the blockchain to facilitate, verify, or negotiate a contract agreement. The transactions only complete when all the conditions in smart contract automatically are met.

For example, if a consumer wanted to purchase power at 20$ per kWh, the smart contract would only be activated when a seller was willing to meet every condition and deliver the power. Additionally, payments are made daily to sellers via the platform.
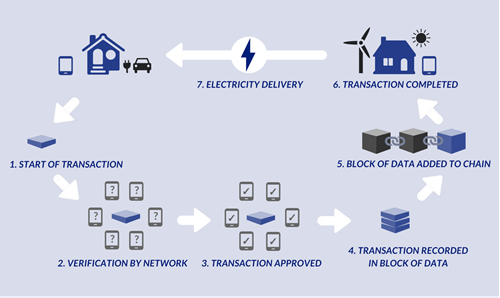
Thanks to blockchain,the efficiency of trading improves and the cost of buying and selling energy significantly decrease. Also, blockchain is able to incorporate internal smart meters, where computers could automatically consider demands and supplies in real time to balance the grid. While the technology is still in its early days, it is undeniable that blockchain has the huge potential in P2P energy trading.
II. Impacts of P2P energy trading

Benefits of P2P energy trading
Based on the operation of P2P energy trading system, it is clear that everyone can take advantage of this innovative technology because of its potential and financial benefits.
- Making own decision for dealing with available consumers instead of the middle man (electricity retailers).
- Can decide to either sell the energy or donate it to support neighborhood or gornvernment.
- Save the cost of electricity consumption as well as the operation cost. It is a win-win situation for both consumers and producers.
- All transactions are public and once on the blockchain, they cannot be altered in any way, which means all contracts are secured.
Disadvantages of P2P energy trading
However, while P2P energy trading has various advantages, the biggest concern about that concept is the huge cost for installation the system at the beginning. Greenmatch (2019) explained the reason for the high initial cost of setting solar energy system that the cost includes paying for solar panels, inverter, batteries, wiring, and for the installation.
Apart from the expensive cost, the space for setting up solar power system is another problem. The more electricity you want to generate, the more solar panels you need to install. Solar panels require a lot of space and some roofs are not big enough to fit the expected number of solar panels.
Although P2P energy trading system has its own pros and cons, that idea has contributed a lot to the changes in ways people use and sell energy. However, P2P energy trading is still in its infancy and is not commercialised yet. There are still a lot of projects and trials in the world with new methods and concepts to approach this innovative idea.
While P2P energy trading may not be at the stage of mass integration yet, the idea is quickly being adopted as a solution for the future. By revolutionising this technology, consumers will no longer have to depend on utility retailers for their energy, and can make smart, sustainable choices about the way of effectively control their energy usage (InfiniteEnergy 2019).
Reference
InfiniteEnergy 2019, What is Peer-to-peer energy trading?, InfiniteEnergy, retrieved 16 December 2019, < https://www.infiniteenergy.com.au/peer-to-peer-energy-trading/ >
Winfred K. Mandela n.d, Understanding P2P Energy Trading, The Startup, retrieved 16 December 2019, < https://medium.com/swlh/understanding-p2p-energy-trading-a477eb7b55e0 >
Barbara Albert 2018, Peer-to-peer trading explained, 100% Renewable, retrieved 18 December 2019, < https://100percentrenewables.com.au/peer-to-peer-energy-trading/ >
Sumitomo Corporation of Americas 2019, Sumitomo Corporation Group Invests In Microgrid Innovator LO3 Energy, CISION PR Newswire, retrieved 20 December 2019, < https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/sumitomo-corporation-group-invests-in-microgrid-innovator-lo3-energy-300881978.html >
Greenmatch 2019, What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Solar Power?, Greenmatch, retrieved 20 December 2019 < https://www.greenmatch.co.uk/blog/2014/08/5-advantages-and-5-disadvantages-of-solar-energy#cost >
Luke Fortney 2019, Blockchain Explained, Investopedia, retrieved 20 December 2019, < https://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/blockchain.asp >
SUNPOWER n.d, What is Solar Energy and How Do Solar Panels Work?, SUNPOWER, retrieved 20 December 2019, < https://us.sunpower.com/what-solar-energy-and-how-do-solar-panels-work >